账号保存
谈到linux的账号认证,其实就是如何保存于通过口令(password)鉴别,这里首先要讲两个文件,一个是/etc/passwd,另外一个是/etc/shadow文件
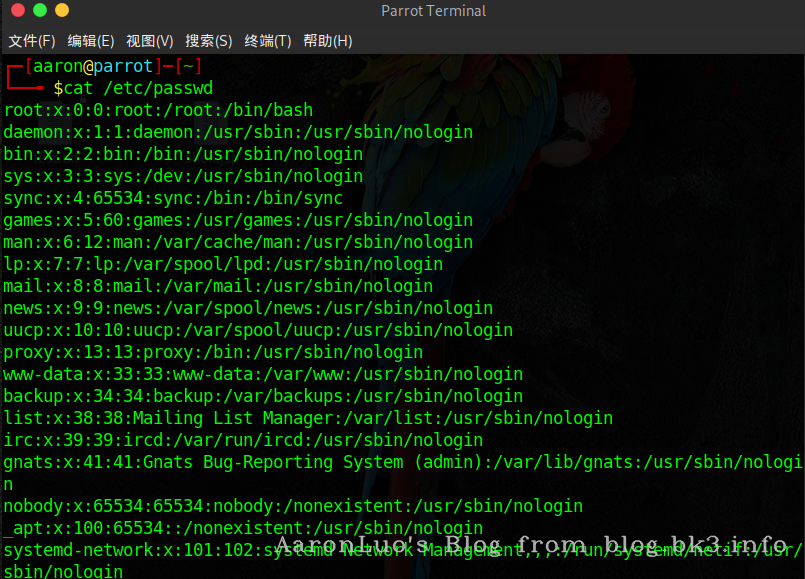
我们先来看/etc/passwd 文件
/ect/passwd
我们来解释一下这张图片,说明一下/etc/passwd文件的格式:用户名:口令:用户标识号:组标识号:注释性描述:主目录:登录Shell,我们来说几个重点字段
- 口令: 因为安全问题,放在/etc/shadow中去了
- 用户标识号:uid
- 组标识号:gid
- 主目录:用户主目录
- 登录shell:当为nologin的时候其实是无法登录的
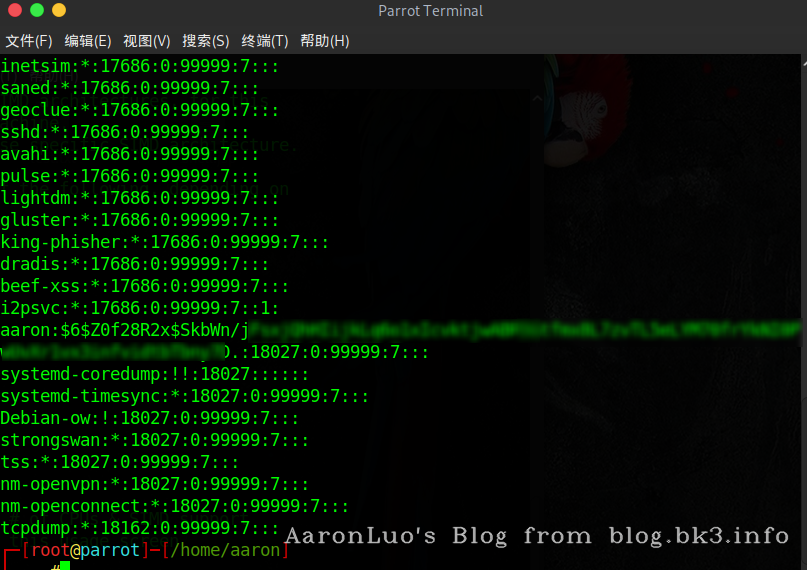
/ect/shadow
我们来解释一下这张图片,说明一下/etc/shadow文件的格式:用户名:$加密方式$盐字符串$密文口令:最后一次修改时间:最小时间间隔:最大时间间隔:警告时间:不活动时间:失效时间:标志,我们来说几个重点字段。
- 加密方式:6->sha-512加密,1->md5加密,2->Blowfish加密,5->sha-256加密
- 盐:加盐对抗破解的那个随机字符串
- 密文口令:和盐一起经过f(password,key)运算后得到的值
认证流程
linxu引导启动后,会读取前文介绍的两个文件,读取到内存中,存入两个数据结构中(passwd结构和spwd结构),使用linux自身的函数获取用户名和密码,对密码进行运算后进行比较。从数学公式来讲,如下: value = f(InputPasswd,SaltString) 然后比较这个value的值与/etc/shadow中的值保存的是否一致。
破解方式
原理介绍
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
const char *value = "";//这里是/etc/shadow中的hash值
const char *password = "";//明文密码
const char *salt = "";
int main(){
if (strcmp(value,crypt(password,salt)) == 0){//salt是盐的字符串
printf("[*]Shadow-Hash-Value: %s\n",value);
printf("[*]Count-Hash-Value: %s\n",crypt(password,salt));
printf("[*]Find-Password:%s\n", password);
}
return 0;
}
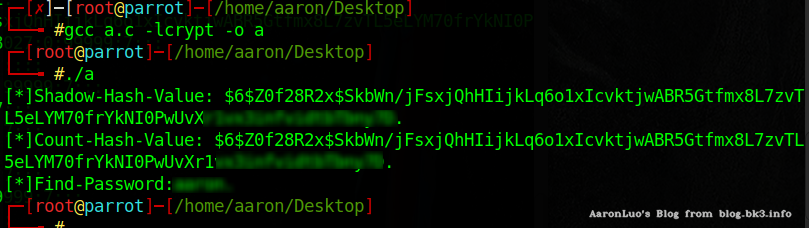
Test
# gcc a.c -lcrypt -o a
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
const char *value = "$6$Z0f28R2x$SkbWn/jFsxjQhHIijkLq6o1xIcvktjwABR5Gtfmx8L7zv******************.";//这里是/etc/shadow中的hash值
const char *password = "xx";//明文密码
const char *salt = "$6$Z0f28R2x$";
int main(){
if (strcmp(value,crypt(password,salt)) == 0){//salt是盐的字符串
printf("[*]Shadow-Hash-Value: %s\n",value);
printf("[*]Count-Hash-Value: %s\n",crypt(password,salt));
printf("[*]Find-Password:%s\n", password);
}
return 0;
}